Describe How Acteria Use the Host Cell's Cytoskeleton
We have step-by-step solutions for. Pages 256 This preview shows page 106 - 118 out of 256 pages.

Deep Phenotypic Mapping Of Bacterial Cytoskeletal Mutants Reveals Physiological Robustness To Cell Size Current Biology
In conclusion major events in bacterial lifecycles require host cytoskeletal components and.

. Secrete effectors that rearrange the host cells cytoskeleton causing pedestals. In the case of the zipper mechanism engagement of bacterial proteins with host membrane proteins normally involved in cellular adhesion such as cadherins or integrins leads to the recruitment of various host factors involved in the strengthening of cellcell or cell-matrix contacts. Without crescentin the cells adopt a.
WTAMU Fall 2020 Learn with flashcards games and more for free. Membrane-targeted bacterial effector proteins might trigger actin polymerization through diverse mechanisms during cell entry by bacterial pathogens. Avoidance of IS eg.
The molecular details of how Chlamydia co-opts the cytoskeleton is becoming clearer with bacterial factors and their corresponding. PENETRATION INTO THE HOST CELL CYTOSKELETON -some bacteria produce surface proteins called invasins that rearrange actin filaments of the cytoskeleton -this causes membrane ruffling bacteria sinks into the ruffle and is engulfed by host cell -then it uses actin to move from one cell to the next Describe the function of siderophores SIDEROPHORES. Intracellular bacteria further manipulate the actin cytoskeleton to exit host cells by lysis or vacuole extrusion.
A common target of all Chlamydia species studied so far is the host cell cytoskeleton with past and recent findings revealing crucial roles in invasion inclusion maintenance nutrient acquisition and egress. Trypanosoma Neisseria Penetration into the Host Cell Cytoskeleton. Some of these may aid in the infection process some of the host structures could be used by microbes to establish disease and some of these could be used by the microbe to resist the immune system or antimicrobial chemotherapy.
Textbook solution for Microbiology. Direct modulation of the host cell cytoskeleton by Salmonella actin-binding proteins. How is DNA RNA proetin and lipid synethsis.
Here we describe a bacterial equivalent to IF proteins named crescentin whose cytoskeletal function is required for the vibrioid and helical shapes of Caulobacter crescentus. Intracellular bacteria actively manipulate the host actin cytoskeleton to facilitate major lifecycle events such as cellular. Intermediate filaments IFs of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton play an important role in cell shape in higher organisms.
Course Title EXAM 3. Tortora Chapter 15 Problem 7LO. 1 Plasma membrane 2 Cytoskeleton 3 Host ribosome 4 Nucleus 5 Endocytosis Expert Answer.
Identify 6 mechanisms of avoiding destruction by phagocytosis. Secrete effectors that rearrange the host cells. According to Bhavsar Guttman and Finlay 827 different intracellular microorganisms take advantage of the components found within cytoskeleton to gain entry into host cells.
Describe how bacteria use the host cells cytoskeleton to enter the cell Bacteria rearranges the actin filaments of the cytoskeleton with invasion surface protein that causes a ruffling which engulfs the bacteria and get in cell. Intracellular bacteria use host actin for diverse infection events. A common strategy employed by Skip to content.
This effect is called membrane ruffling the result of disruption in the cytoskeleton of the host cell. Coli produce invasins proteins that cause the actin of the host cells cytoskeleton to form a basket that carries the bacteria into the cell. The molecular strategies used by bacteria to interact with the host can be unique to specific pathogens or conserved across several different species.
M protein of S. Trends in Cell Biology. Ability to escape from a phagosome.
An Introduction 13th Edition 13th Edition Gerard J. When Ecoli makes contact with a host cell invasins of the MO cause the appearence of the host cell plasma membrane to resemble the splash of a drop of a liquid hitting a solid surface. Others remain extracellular but manipulate host pathways from outside.
The MO sinks into the ruffle and is engulfed by the host cell. Eukaryotic cells have cytoskeleton consisting of intermediate and. Due to the small size of bacteria induction of a response normally strengthening cell.
Manipulation of cytoskeleton is another mechanism used by intracellular bacterial pathogen to infect and replicate within the host cell. How are cellular processes compartmentalized. Some bacterial pathogens gain entry and subvert immune detection by surviving intracellularly.
Pathogenic bacteria utilise a number of mechanisms to cause disease in human hosts. Remodeling of the host cytoskeleton is a common strategy employed by bacterial pathogens. Bacterial pathogens express a wide range of molecules that bind host cell targets to facilitate a variety of different host responses.
No such filaments have been found in prokaryotes. Students who viewed this also studied. Describe how bacteria use the host cells cytoskeleton to enter the cell - the microfilaments of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton are composed of a protein called actin which is used by some microbes to penetrate host cells and by others to move through and between host cells.
Other intracellular bacteria stimulate actin polymerization and form actin tails that aid bacterial movement within the host cytosol and propulsion into neighboring cells. Although there is vigorous investigation of the cell biology underlying these bacterially mediated cytoskeleton modifications knowledge of the plasticity and dynamics of the bacterial signaling networks that regulate the expression of genes necessary for these phenotypes is lacking.
How Are Bacteria Cells And Animal Cells Alike Quora

The Bacterial Cytoskeleton The Only Cytoskeletal Element Present In Download Scientific Diagram

Bacterial Filament Systems Toward Understanding Their Emergent Behavior And Cellular Functions Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Schematic Illustration Of The Different Bacterial Cell Walls And Their Download Scientific Diagram

Mechanical Genomics Identifies Diverse Modulators Of Bacterial Cell Stiffness Cell Systems
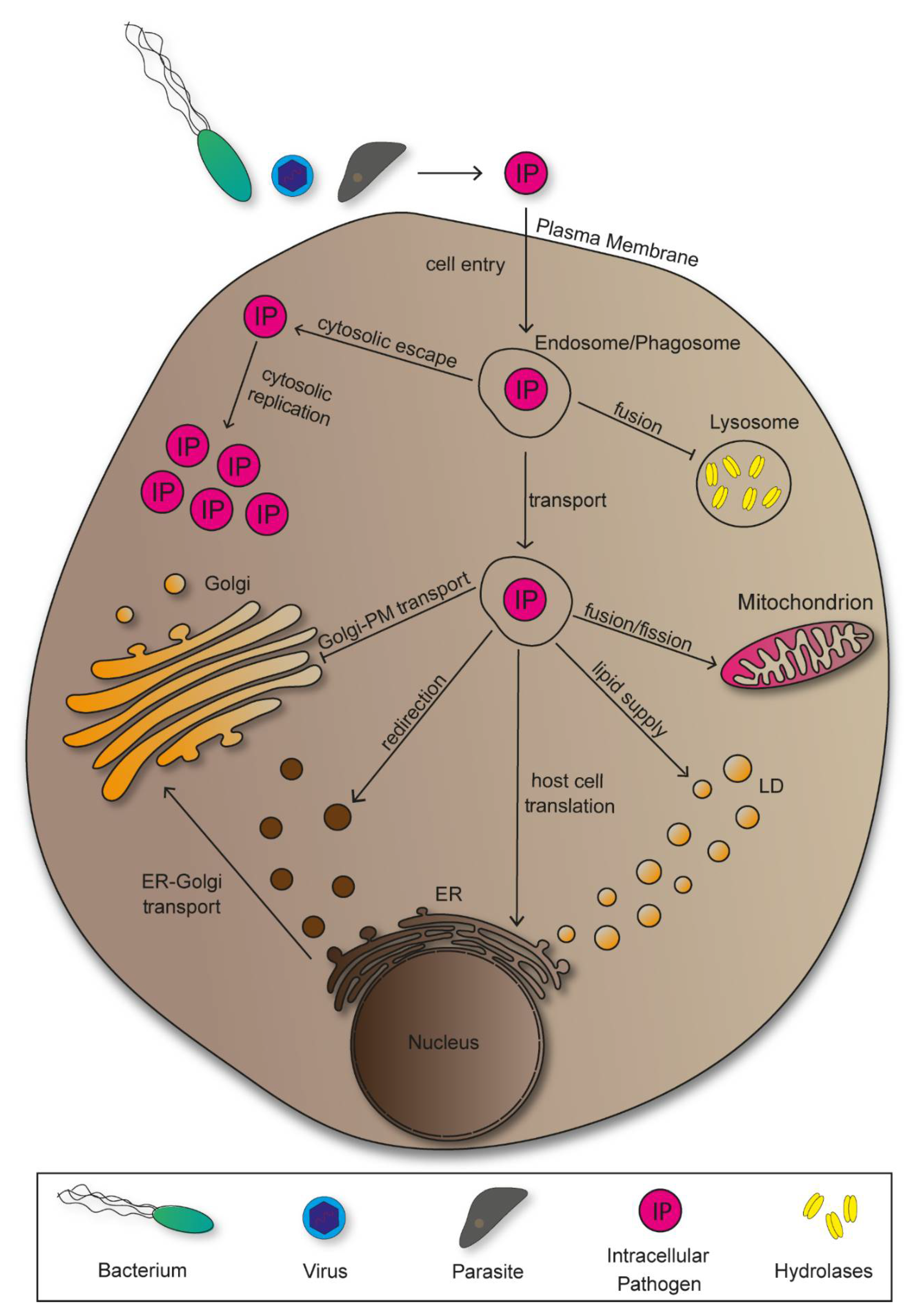
Ijms Free Full Text Manipulation Of Host Cell Organelles By Intracellular Pathogens Html

Deep Phenotypic Mapping Of Bacterial Cytoskeletal Mutants Reveals Physiological Robustness To Cell Size Current Biology

Bacterial Cell Wall An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
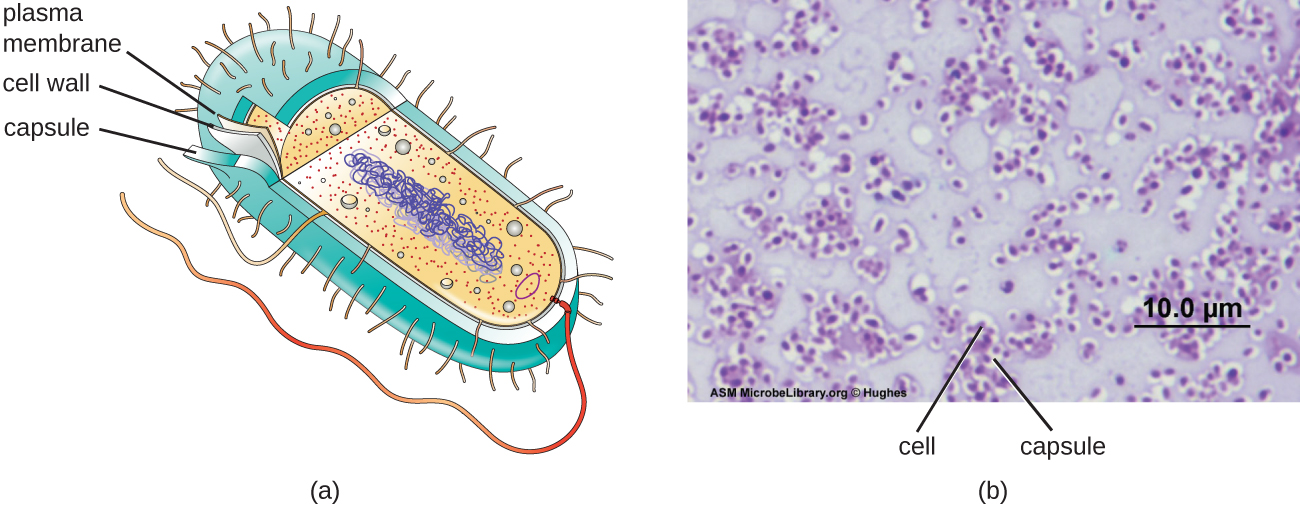
2 2 Unique Characteristics Of Prokaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts
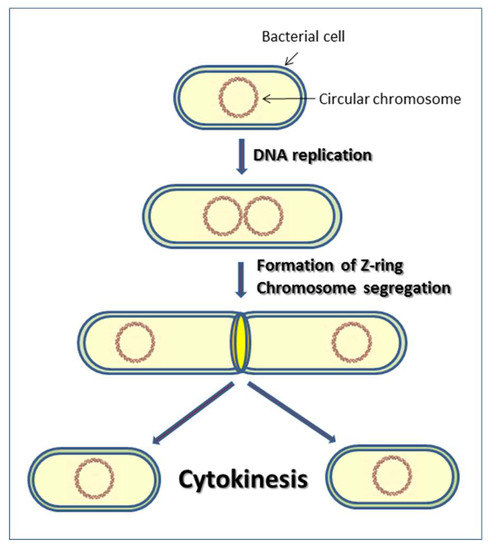
Cells Free Full Text The Cell Wall Hydrolytic Nlpc P60 Endopeptidases In Mycobacterial Cytokinesis A Structural Perspective Html

Cell Walls Of Prokaryotes Boundless Microbiology

Bacterial Cytoplasmic Membrane Components Structure Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
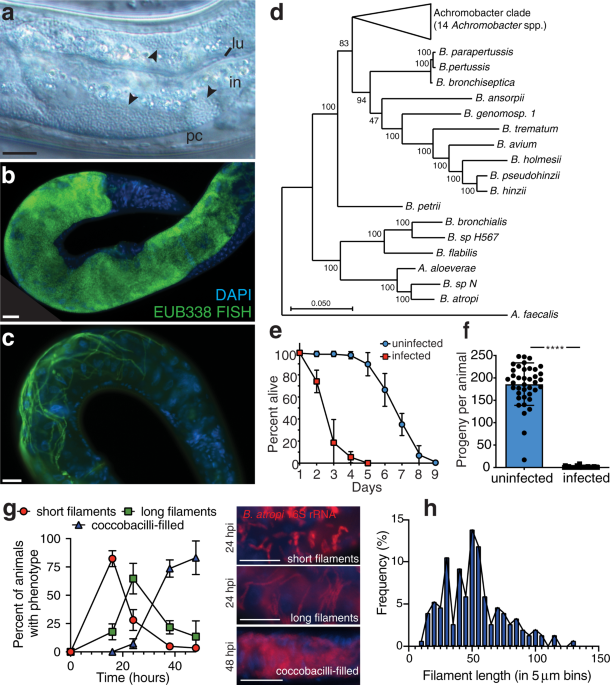
Bacterial Filamentation As A Mechanism For Cell To Cell Spread Within An Animal Host Nature Communications

Spatial Organization Of Transcription In Bacterial Cells Trends In Genetics

Bacterial Factors Required For Septin Cage Entrapment In Actively Download Scientific Diagram

Bacterial Cell Diagram By Russell Kightley Media

A Landmark Protein Essential For Establishing And Perpetuating The Polarity Of A Bacterial Cell Cell

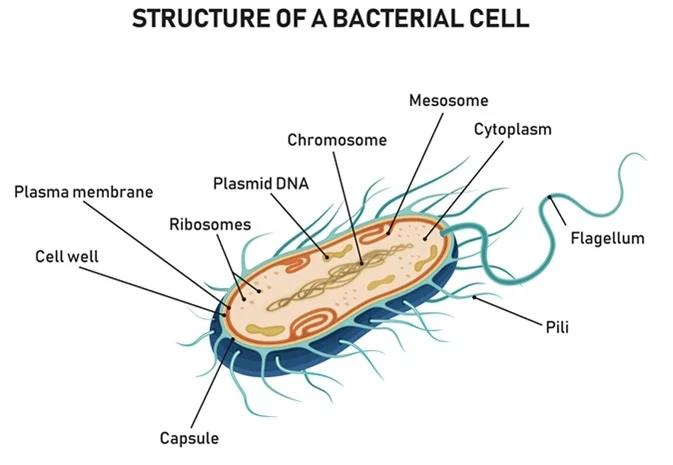
The Schematic Diagram Of Bacterial Cell Structure Download Scientific Diagram Bacterial Cell Structure Cell Diagram Cell Structure
Comments
Post a Comment